Distributed Control System
Why
DCS
Ø For Total Plant
Automation
Ø For Higher
Productivity
Ø For Optimal
Process Control
Ø For Advance
Process Control
Ø For Regulatory
Compliance
Ø For Management
information System
Ø In Tune with
Global Requirement
What
is DCS System
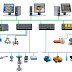
A distributed
control system (DCS) is a specially designed automated control system that geographically and functionally distributed
all over the plant or control area. It is specially designed with redundancy and diagnostic
capabilities to improve control reliability and performance. It gives greater
flexibility to control distributed discrete field devices and its operating
stations
Distributed Control System is a specially designed
control system used to control complex, large and geographically distributed
applications in industrial processes. In this, controllers are distributed
throughout the entire plant area. These distributed controllers are connected
to both field devices and operating PCs through high speed communication
networks as shown in figure.
It differs from
the centralized control system wherein a single controller at central location
handles the control function, but in DCS each process element or machine or
group of machines is controlled by a dedicated controller. DCS consists of a large
number of local controllers in various sections of plant control area and are
connected via a high speed communication network.
In DCS control
system, data acquisition and control functions are carried through a number of
DCS controllers which are microprocessor based units distributed functionally
and geographically over the plant and are situated near area where control or
data gathering functions being performed as shown in the figure above. These
controllers able to communicate among themselves and also with other
controllers like supervisory terminals, operator terminals, historians, etc.
Distributed
individual automatic controllers are connected to field devices such as sensors
and actuators. These controllers ensure the sharing of gathered data to other
hierarchal controllers via different field buses. Different field buses or
standard communication protocols are used for establishing the communication
between the controllers. Some of these include Profibus, HART, arc
net, Modbus, etc.
DCS is most
suited for large-scale processing or manufacturing plants wherein a large
number of continuous control loops are to be monitored and controlled.
Nowadays, distributed control system has been found in many industrial fields
such as chemical plants, oil and gas industries, food processing units, nuclear
power plants, water management systems, automobile industries, etc.
Features of DCS:
Ø Reduce System Failure: Control
function is distributer among multiple CPUs (Field Control Stations). Hence
failure of one FCS does not affect the entire plant.
Ø Sophisticated
HMI: Use color CRT
with outstanding resolution. Trending, logging and graphical representation of
the HMI’s give effective user interface.
Ø Redundancy is
available at various level.
Ø Superior Reliability: Due to
redundancy and partitioning it ensures an outstanding level of reliability,
performance and expandability.
Ø
Broad Flexibility and
expandability: Structure of DCS can
be scalable based on the number of I/O’s from small to large system by accommodating additional stations.
Ø System security:
Security is also provided at different levels such as engineer level,
entrepreneur level, operator level, etc.
Ø Interlocks: Instruments
and interlocks are created by software. Generation and modification of the interlocks are very
flexible and simple
Ø Easy system maintenance: In the
unlikely event of failure, a self diagnostic function quickly locates the source of the problem,
Modular component design permits easy replacement .Maintenance and
troubleshooting become very easy.
Ø Minimize
production cost: To increase reliability, productivity and
quality while minimizing the production cost.
Ø
Powerful alarming
system of DCS helps operators to respond
more quickly to the plant conditions
Ø Cost
effective in the long run.
Ø Information
regarding the process is presented to the user in various format.
Ø Field wiring
is considerably less
Working & Operation of DCS System
The operation of
DCS goes like this; Sensors senses the process information and send it to the
local I/O modules, to which actuators are also connected so as to control the
process parameters. The information or data from these remote modules is
gathered to the process control unit via field bus. If smart field devices are
used, the sensed information directly transferred to process control unit via
field bus.
The collected
information is further processed, analyzed and produces the output results
based on the control logic implemented in the controller. The results or
control actions are then carried to the actuator devices via field bus. The DCS
configuring, commissioning and control logic implementation are carried at the
engineering station. The operator able to view and send control actions
manually at operation stations.
Architecture of DCS:
Architecture of DCS are almost same for all manufactures
with a little difference. Here is a
architecture of DCS from Yokogawa model CENTUM CS 3000
Human Interface Station
(HIS)
HIS is the
operating station, is used to operate,
monitor and control plant parameters. It can be a PC or any other
monitoring device that has a separate software tool on which operator can view
process parameter values and accordingly to take control action.
Operating
stations can be a single unit or multiple units where a single unit performs
functions like parameter value display, trend display, alarming, etc. while
multiple units or PCs performs individual functions such as some PCs display
parameters, some for trend archives, some for data logging and acquiring, etc.
Engineering Station (ENG)
Engineering
station is a PC with engineering capabilities used for system configuration and
system maintenance.
It is the
supervisory controller over the entire distributed control system. It can be a
PC or any other computer that has dedicated engineering software
This engineering
station offers powerful configuration tools that allow the user to perform
engineering functions such as creating new loops, creating various
input and output points, modifying sequential and continuous control
logic, configuring various distributed devices, preparing
documentation for each input/output device, etc.
Field Control Station
(FCS)
Field control station is the control unit for plant
process control. Varying with the application capacities and application
usages, there are several types of field control stations in the lineup. Controllers are distributed geographically in various
section of control area and are connected to operating and engineering stations
which are used for data monitoring, data logging, alarming and controlling
purpose via another high speed communication bus.
These
communication protocols are of different types such as foundation filed bus,
HART, Profibus, Modbus, etc. DCS provides information to multiple displays for
user interface.
Safety Control Station
(SCS)
Safety control
station is a controller of the ProSafe-RS TÜV SIL3 certified safety
instrumented system and it can be configured on the same network with CENTUM CS
3000 enabling HIS to monitor status of ProSafe-RS.
I/O Modules
Varieties of
Fieldnetwork I/O (FIO) are available in compact sizes to convert process
signals for FCS formats. Remote I/O are
for remote input and output that passes the field signals to FCS control unit
via remote buses.
Bus converter (BCV)
Bus converters
are used to link multiple domains.
System Integration OPC
Station (SIOS)
SIOS serves as a
gateway for connecting CENTUM CS 3000 R3 system and the OPC server to the
third-party PCS. It exchanges data, and acquires alarms and events through the
OPC server.
Control Network (Vnet/IP)
A real-time
control network for linking the stations such as FCS, HIS, and BCV.
Field Digital Network
CENTUM CS 3000
R3 supports field digital protocols such as FOUNDATION fieldbus, HART, PROFIBUS,
DeviceNet, Modbus, Modbus/TCP, EtherNet/IP and ISA100 wireless.
Controller
Yokogawa
controllers are designed for controlling and monitoring industrial plants which
must keep running non-stop in stabilized status with high reliabilities.
DCS Systems from Different Vendors
Some of the available DCS systems
include
Ø
ABB- Freelance 800F and 800xA, Freelance 2000
Ø
Yokogawa - Micro Excel ,
Centum Excel, Centum CS 1000, CS 3000, Centum VP
Ø
Honeywell -TDC 3000,
Experion PKS, TPS, GUS
Ø
Emerson - Delta V Digital
Automation
Ø
Siemens - Simatic PCS 7
Ø
Allen Bradley - NetLinx
Ø
Foxboro –I/A Series
Ø Moore
– APACS
PLC
and DCS a Relative study:
Ø DCS
was developed as a replacement of ‘PID controller’, whereas PLC was developed
for the replacement of ‘Relay Logic’.
Ø PLC
is mainly used for small application, whereas DCS is used for large
application.
Ø Both
PLC and DCS are used for ‘logic’ and ‘continuous controller’. But PLC is mainly
used for Logic where as DCS is mainly used for continuous control.
Ø Scan
time of PLC is less than DCS. So PLC is faster than DCS.
Ø DCS
must have redundancy but PLC might not.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 A
cabinet type and a rack-mount type of FCS are available from Yokogawa. Both
Vnet/IP and V net control networks can be used for configuring the system
networks. The dual-redundant design of the FCS processor modules, power supply,
I/O modules, and I/O networks achieve high availability of 99.99999%. The pair
& spare architecture is unique to Yokogawa that improves the stability of
process control.
A
cabinet type and a rack-mount type of FCS are available from Yokogawa. Both
Vnet/IP and V net control networks can be used for configuring the system
networks. The dual-redundant design of the FCS processor modules, power supply,
I/O modules, and I/O networks achieve high availability of 99.99999%. The pair
& spare architecture is unique to Yokogawa that improves the stability of
process control.
Process I/O Modules
Fieldnetwork I/O (FIO)
Yokogawa offers compact, cost-effective, and reliable I/O devices, targeted as the industrial standard.
Yokogawa offers compact, cost-effective, and reliable I/O devices, targeted as the industrial standard.
Subsystem Integration
In order to operate and monitor
the subsystems of the auxiliary devices controlled by programmable logic
controller (PLC), various types of analyzers and other instruments for the
integrated plant automation, FCS subsystem communication capability enables
connection with the subsystems, and also supports dual-redundant configuration.
The subsystems include Mitsubishi
MELSEC, Allen Bradley PLC-5 and SLC500, Modbus compatible devices, Siemens
SIMATIC, Omron SYSMAC, Yokogawa FA-M3, Darwin, and DAQSTATION and so on.
.
Human Machine Interface
Human Interface Station
(HIS)
 Operators
access production control system via CENTUM CS 3000’s human interface station
(HIS) to make fast and intelligent decisions that maximize performance and
minimize risks.
Operators
access production control system via CENTUM CS 3000’s human interface station
(HIS) to make fast and intelligent decisions that maximize performance and
minimize risks.
Based on the ergonomic design
concept, the HIS can be selectable from desk top, open display style console,
and enclosed display style console types. Multiple monitors can be set, and
each one of the monitor displays multiple operation windows.
Dedicated Operation
Keyboard
 The
operation keyboard is unique to Yokogawa. It consists of alphanumeric keys and
special operation keys which are assembled with the dustproof and drip-proof
flat keys. By assigning graphics to each button, operators can call up a
graphic by one touch.
The
operation keyboard is unique to Yokogawa. It consists of alphanumeric keys and
special operation keys which are assembled with the dustproof and drip-proof
flat keys. By assigning graphics to each button, operators can call up a
graphic by one touch.
Operation Windows
There
are different window like Graphic window, Control window, Overview window,
Trend window
|
|
Screen Modes
The ‘Multiple-window mode’ like
an office PC and the ‘Full-screen mode’ like the legacy operator console are
available for operation and monitoring environment.
Open Interface
The process control industry
standard open interface OPC (OLE for Process Control, or open productivity &
connectivity) is provided for collecting the process data, trend data and
messages.
Access Control
To prevent operation errors and
other problems and ensure the safety of the system, such as prohibiting
operations by unauthorized persons, limiting the ranges of operation and
monitoring, and restricting operator actions to the system, extensive security
functions are applied.
.
___________________________________________________________________________
Process
Control Unit of DCS
It is also called
as a local control unit, distribution controller, or process station. A
distributed control system can consists of one or more process stations that
can be extended with different types of I/O units. These controllers consist of
a powerful CPU module, field bus or communication module with extended field
bus capability and either direct or remote connected I/Os.
The field devices like sensors
and actuators are connected to I/O modules of this unit. Some field devices can
be directly connected to field bus (such as Profibus) without any I/O module,
which can be termed as smart field devices.

These units acquire the information
from various sensors via input module, analyze and process it based on the
control logic implemented and sends the output signals via output modules to
have control on actuators and relays.
This acts as process station,
which is responsible for acquiring and controlling the data from the process.
This unit consists of a power supply along with CPU section, Ethernet section,
Profibus section and remote communication interface unit for I/Os interfacing
as shown in the figure where first module is AC 800F unit and other one is
remote I/O (also called as communication interface module).
Communication System
The
communication medium plays a major role in the entire distributed control
system. It interconnects the engineering station, operating station, process
station and smart devices with one another. It carries the information from one
station to another. The common communication protocols used in DCS include
Ethernet, Profibus, Foundation Field Bus, DeviceNet, Modbus, etc.
It is not
mandatory to use one protocol for entire DCS, some levels can use one network
whereas some levels use different network. For instance, consider that field
devices, distributed I/Os and process station are interconnected with Profibus
while the communication among engineering station, HMI and process station
carried though Ethernet as shown in the figure below.

The major
advantage of DCS is the redundancy of some or all levels of the control
area. Most of the cases critical processes are installed with redundant
controllers and redundant communication networks such that problem in main
processing line should not affect the monitoring and control functions because
of the redundant processing section.
Smart or Intelligent Devices
The intelligent
field devices and field bus technology are advanced features of DCS technology
that replaces traditional I/O subsystems (I/O modules). These smart devices
embed the intelligence required for simple sensing and control techniques into
the primary sensing and actuating devices. And hence it replaces the need for a
DCS controller to perform routine sensing and control process.
These field devices can be
directly connected to field bus so that sourcing of multiple measurements to
the next higher level control station is possible via digital transmission line
by eliminating extraneous hardware such as local I/O modules and controllers.
Difference
between SCADA and DCS (DCS vs SCADA)
Although both
DCS and SCADA are monitoring and control mechanisms in
industrial installations, they have different goals. There exist some
commonality between DCS and SCADA in terms of hardware and its components,
however, there are certain requirements by the end applications that separates
a robust and cost-effective DCS from the viable SCADA system. Some of the
differences between DCS and SCADA are listed below.

1. DCS is process oriented, whereas SCADA is
data-gathering oriented. DCS emphasizes more on control of the process and it
also consists of supervisory control level. And as a part of doing so, it
presents the information to the operator. On the other hand, SCADA concentrates
more on acquisition process data and presenting it to the operators and control
centre.
2. In DCS, data acquisition and control modules
or controllers are usually located within a more confined area and the
communication between various distributed control units carried via a local
area network. SCADA generally covers larger geographical areas that use
different communication systems which are generally less reliable than a local
area network.
3. DCS employs a closed loop control at process
control station and at remote terminal units. But in case of SCADA there is no
such closed loop control.
4. DCS is process state driven where it scans the
process in regular basis and displays the results to the operator, even on
demand. On the other hand, SCADA is event driven where it does not scan the
process sequentially, but it waits for an event that cause process parameter to
trigger certain actions. Hence, DCS does not keep a database of process
parameter values as it always in connection with its data source, whereas SCADA
maintains a database to log the parameter values which can be further retrieved
for operator display and this makes the SCADA to present the last recorded
values if the base station unable to get the new values from a remote location.
5. In terms of applications, DCS is used for
installations within a confined area, like a single plant or factory and for a
complex control processes. Some of the application areas of DCS include
chemical plants, power generating stations, pharmaceutical manufacturing, oil
and gas industries, etc. On the other hand SCADA is used for much larger
geographical locations such as water management systems, power transmission and
distribution control, transport applications and small manufacturing and
process industries.
In spite of these major differences, the
modern DCS and SCADA systems come with common standard facilities while dealing
process plant automation. However, the choice between DCS and SCADA depends on
its client and end application requirement. But if the client choice between
these two, by gaining equal requirement from the process, DCS is the economical
choice as it help to reduce the cost and offer better control.
Foxboro I/A Series
The following figure is the basic
architecture of Foxboro I/A Series system

Siemens PCS7
The following figure is the basic
architecture of Siemens PCS7

Honeywell Experion PKS
The following figure is the basic
architecture of Honeywell Experion PKS

Honeywell TDC3000
The following figure is the basic
architecture of Honeywell TDC3000

Honeywell Total Plant
Solutions (TPS)
The following figure is the basic
architecture of Honeywell TPS

Yokogawa Centum CS3000
The following figure is the basic
architecture of Yokogawa Centum CS3000

What
is Distributed Control System
7
Important features of DCS
•
To handle complex processes:
In
factory automation structure, PLC-Programming Logic
Controller is used to
control and monitor the process parameters at high speed requirements. However
due to limitation of number of I/O devices, PLC’s cannot handle complex
structure.
System
redundancy:
System
Redundancy
CENTUM CS3000 R3
Application of Windows
Technology
With Windows Remote Desktop
capability, plant operation, monitoring, and engineering can be performed from
a personal computer in your office or at a remote field location without any
additional software.
Remote Operation and
Monitoring
The same HIS displays in the control room can be shown on the PC in your office. For production facilities in remote locations around the world, remote operation and monitoring can be simply structured.
The same HIS displays in the control room can be shown on the PC in your office. For production facilities in remote locations around the world, remote operation and monitoring can be simply structured.
Remote Engineering
The engineering work for modification can be performed remotely via a network, eliminating the need for dispatching engineers and reducing both maintenance and engineering cost.
The engineering work for modification can be performed remotely via a network, eliminating the need for dispatching engineers and reducing both maintenance and engineering cost.


DCS
 Reviewed by Suvodeep Roy
on
16:26
Rating:
Reviewed by Suvodeep Roy
on
16:26
Rating:
 Reviewed by Suvodeep Roy
on
16:26
Rating:
Reviewed by Suvodeep Roy
on
16:26
Rating:




















No comments: